Mutilcore Processor: A multi-core processor is a single computing component with two or more independent actual processing units (called “cores”), which are units that read and execute program instructions. The instructions are ordinary CPU instructions (such as add, move data, and branch), but the single processor can run multiple instructions on separate cores at the same time, increasing overall speed for programs amenable to parallel computing. Below is a sample diagram of the multicore architecture.
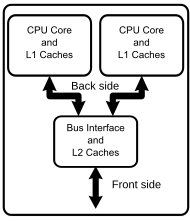
Examples: AMD (A-Series,Athlon II,FX-Series,Phenom,Epyc); IBM(POWER 4, POWER 5, POWER 6), Intel (Core 2 Duo, Core i3, Core i5, Core i7)
Manycore Processor: Manycore processors are specialist multi-core processors designed for a high degree of parallel processing, containing a large number of simpler, independent processor cores (e.g. 10s, 100s, or 1,000s). Manycore processors are used extensively in embedded computers and high-performance computing.
Examples: Sunway TahiuLight (Chinese Supercomputer), GPU’s, Intel Xeon Phi, Tilera, Teraflops Research Chip, etc.
